
You can restore a deleted partition using the rescue tool available in parted:
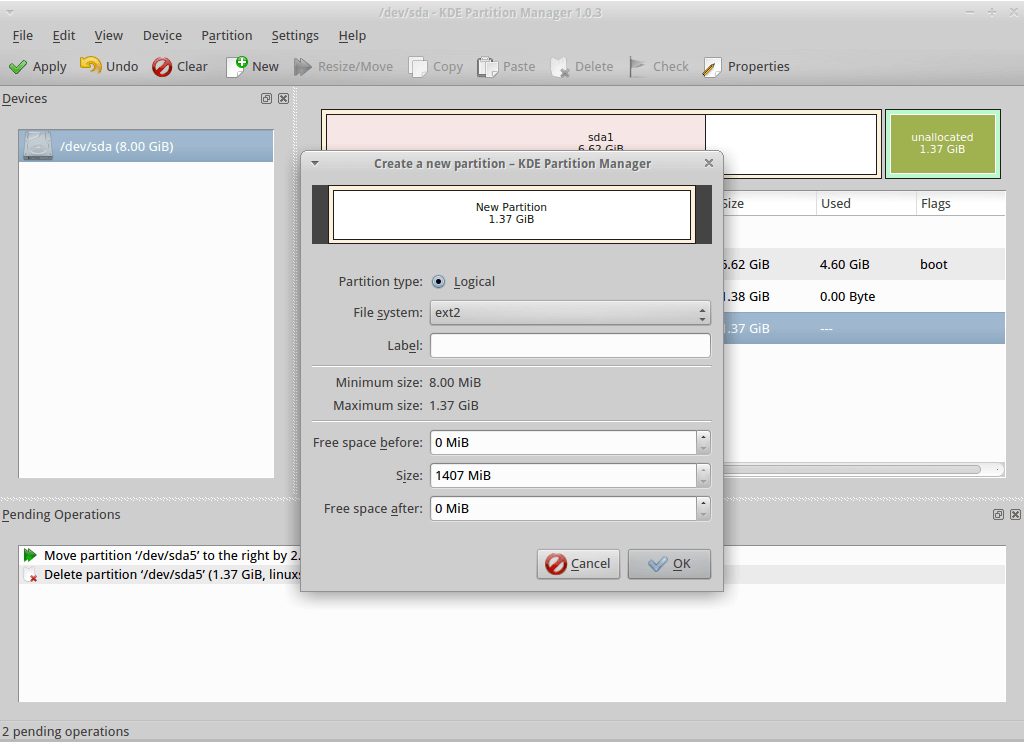
How to Restore Accidentally Deleted Disk Partition with Rescue? Sector size (logical/physical): 512B/512Bīe careful with the command, since it doesn’t require to confirm removal. The command will remove the partition with the number 1: (parted) print If you want to remove a partition on a disk, you can use the rm command in parted: You can set the one you want:įor example, let’s mark the partition as bootable: You can also change a partition flag in parted. To reduce the file system size, the following commands are used. If you shrinking the partition size, you have to reduce the file system size first, and then reduce your partition. Run the following command in parted:įirst, extend the partition, and then expand the file system on it. You can resize a partition interactively. To extend or shrink a partition size, the resizepart subcommand is used in parted. How to Resize (Extend or Shrink) Partition with Parted? Thus, you can make your work easier or add similar commands to bash scripts or kickstart files. Using the command, we will create a partition on vdb disk and allocate all free space to it. # parted -a opt /dev/vdb mkpart primary ext4 0% 100% & mkfs.ext4 /dev/vda1 You can create a partition and format it without going into the parted shell. Writing superblocks and filesystem accounting information: doneĬheck the file system of the partition and make sure it has changed (note that the print command displays the list of partitions on the disk, their numbers, type, size and file system). # (parted) mkpart "home part" ext4 2.5GiB 100% You can also set the partition size in % and assign a label: Or specify any partition size as follows: You can create a partition that spans the whole disk: To display the amount of free space left on a disk, use the following command: In our example, we have entered 5,000, it means that a 5 GB partition will be created.
ext2 is offered by default (we will change it later)


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
